ADMINISTRATIVE POLICY
Connie Zhang
Policy Statement
Tulane University Data (University Data) are valuable institutional assets. The use of University Data must be aligned with the administrative, educational, and institutional research missions of the university, regardless of where University Data is used or maintained. The purpose of this policy is to define and provide the framework and rules for how we identify, categorize, store, use, improve, protect and otherwise manage our data.
Purpose and Scope
Tulane University must ensure the strategic use, management, and reporting of University Data. To do this, a data governance program must be in place to provide sound data governance principles and manage the quality, consistency, usability, accessibility, availability, and protection of University Data throughout its lifecycle. This policy endorses these University Data Governance principles:
- University Data are valuable assets, the use of which must be aligned with the administrative, educational, and institutional research functions of the university. Data value is maximized by understanding what we have and using it well.
- The processes using, and decisions made with, University Data should be ethical, efficient, purposeful, documented, clear, consistent, metrics-driven, aligned to university priorities and needs, and regularly reviewed and communicated.
- The University encourages the integration of university data across all units and departments. Consistent with Tulane University’s institutional complexity, various data systems, and different data formats, to result in reduced duplication of data and greater data accuracy.
- All units and departments within the University should facilitate the access and sharing of University Data where appropriate, subject to appropriate security restrictions as established by each Data Trustee and ratified by the Data Governance Council.
- University Data must be used and safeguarded in compliance with federal, state, and local regulations, Tulane. University policies, and relevant contractual obligations.
Applicability of this Policy
This policy applies to:
- The University and all its campuses, schools, colleges, institutes, and administrative and auxiliary units.
- All University Data regardless of form or location of storage.
Therefore, this policy applies to Information Systems and technology resources and University Data contained in or extracted from those systems or resources. In addition, University Data includes the data processed or stored by the University in hosted environments in which the University does not own or operate the technology infrastructure.
All persons or entities, including but not limited to employees, affiliates, and contractors, whether they be part-time or full-time, whose job responsibilities include inputting, safeguarding, retrieving, or using University Data, and those who supervise such individuals are required to follow the terms of this policy and related University policies.
Website Address
Contacts
Definitions
Academic Data: Academic Data is data collected in support of the academic operations of the University, inclusive of information directly related to the individual student. These would include student information such as grades, test scores, attendance, transcripts, financial aid information, and any analytical data collected about students.
Administrative Data: Administrative Data is collected in support of the administrative and business operations of the University, such as the delivery of services to University units and departments. A substantial number of functions at the University incorporate collections of Administrative Data, such as admissions, student financial aid, records/registrar, alumni/advancement, the business office, investment management office, and human resources, including data utilized in Tulane’s EDI initiative.
Chief Privacy and Data Compliance Officer: The Chief Privacy and Data Compliance Officer is responsible for (i) coordinating all activities related to University Data Management and (ii) ensuring that procedures are developed by functional offices to address those cases where a member of the University community seeks permission to access University Data beyond the normal performance of their duties. The Data Trustees will review and ratify the procedures as developed.
Clinical Data: Clinical Data are information, records, and tangible products collected during the course of patient care or as part of a formal clinical trial program. Clinical data would include electronic health records, clinical administrative data, claims data, patient/disease registries, health surveys, and clinical trials data. Clinical data is subject to all requirements documented within this policy as well as any additional requirements found within the Research Data Policy, if applicable, and/or any other clinical policies.
Data Classification: Data Classification refers to the categorization of University Data and the consistent application of security standards based on such categorization.
Data Custodians: The Data Custodians are employees with information technology expertise assigned to each Information System that maintains University Data. Data Custodians (i) oversee the safe transport and storage of data according to requirements of the appropriate classification(s), (ii) ensure data is stored only on official supported Tulane storage mechanisms and locations, (iii) establish and maintain the underlying infrastructure, and (iv) perform activities required to keep the data intact and available to users. In addition, Data Custodians are responsible for working with Data Stewards, the Chief Privacy and Data Compliance Officer, and data support groups to develop automated processes that identify erroneous, inconsistent, or missing data. Data Custodians work with data support groups, the Chief Privacy and Data Compliance Officer, and Data Stewards to resolve data issues.
Data Governance Council: The Data Governance Council establishes overall policies for management and access to University Data. This committee shall be composed of the Data Trustees; shall be chaired by an elected member of the Data Governance Council; shall approve the policies and procedures developed in each functional area by the Data Stewards and Data Trustees to ensure appropriate compliance with this policy and applicable regulations; shall provide oversight of all University processes which capture, maintain, and report on Administrative Data; and shall approve any decisions to archive Administrative Data.
Data Handling: Data Handling refers to the actions that Data Users should take to use, process, transmit, store, archive, and destroy University Data in a secure manner that aligns with the classification of the data.
Data Lifecycle: The progression of stages in which a piece of information may exist between its original creation or collection and final archival or destruction.
Data Stewardship Advisory Group: The Data Stewardship Advisory Group is a university-wide committee, primarily composed of Data Stewards. Designated Data Users may be invited to attend, as appropriate. This group reviews the operational effectiveness of University Data management policies and procedures and makes recommendations to the Data Governance Council for improvement or change. Data Stewards will share best practices during their meetings, as well as raise concerns which cross functional areas. The group is chaired by an elected member of the group. The Data Stewardship Advisory Group must ensure regular and appropriate collaborative communication with Data Users on any operational changes which impact business processes and data.
Data Stewards: Data Stewards are typically operational managers in a functional area with day-to-day responsibilities for managing business processes and establishing the business rules for the Transactional Systems. Data Stewards will collaborate with Data Trustees to set the classification of data within their area of responsibility. Data Stewards are responsible for reviewing and maintaining the data classifications and handling procedures defined in this policy and other related policies. Data Stewards are appointed by the respective Data Trustee.
Data Trustees: Data Trustees are defined as the authorized manager of the data who have planning and policy-making responsibilities for University Data and for the establishment of operational processes to collect and record data per University business rules. The Data Trustees, as a group, are responsible for overseeing the establishment of data management policies and procedures, and for the assignment of data management accountability. Data Trustees will collaborate with Data Stewards to set the classification of data within their area of responsibility. Data Trustees are also responsible for establishing the appropriate levels of training for Data Users who access the data within the Data Trustee’s unit and area of responsibility.
Data Users: Data Users are individuals who access University Data (in connection with their role at Tulane (i.e., student, faculty, staff, etc.) to perform their assigned duties. Data Users are responsible for safeguarding their access privileges, for the use of the University Data in conformity with all applicable University policies, and for securing such data. So that the proper controls are applied, it is the responsibility of each Data User to:
- Know the classification of the Data being used.
- Know the type of University Data being used.
- Follow Tulane IT policies and the appropriate regulatory and security measures (join computer to domain, encryption, etc.)
- Consult the Related Policies for further information.
Information Systems: Information Systems are all computer or electronic resources that are used in the search, access, acquisition, transmission, storage, retrieval, or dissemination of data. In addition, University technology resources are any technology or services that are owned or managed by the University, that connect to the University network, connect to another University technology or service, or store University data or information.
Office of Assessment and Institutional Research: The Office of Assessment and Institutional Research shall be responsible for working with the appropriate Data Stewards to develop definitions of commonly used terms and will define how official University metrics are calculated. Further, in the course of its work, the Office of Assessment and Institutional Research will typically discover data discrepancies and inconsistencies and will promptly report such to the appropriate Data Steward for resolution.
Research Data: Research Data are information, records, and tangible products arising from or associated with research conducted at, under the auspices of, or using the resources of the University. Research Data includes both intangibles (e.g., information and copyrighted works such as software and expressions of information) and tangibles (e.g., cell lines, biological samples collected for research purposes, synthetic compounds, organisms, and originals or copies of laboratory notebooks). Research data is subject to all requirements documented within this policy as well as any additional requirements found within the Governance and Retention of Research Data Policy.
Transactional System: A transactional system is an information processing system which divides work into individual, indivisible operations, called transactions. These transactions involve the collection, modification and retrieval of data.
University Data: University Data is any data or information, regardless of electronic or printed form or location, that is created, acquired, processed, transmitted, or stored by the University. Where appropriate, University Data may be further defined as Administrative, Academic, or Research Data to provide additional management or information security guidance.
Vice President, Information Technology and Chief Information Officer: The Vice President, Information Technology and Chief Information Officer provides technology leadership and advises the Data Governance Council and Data Stewardship Advisory Group about administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to apply to the handling, use, transmission, processing, storage, and destruction of University Data.
Policy and Procedures
It is the policy of the University to implement University a Data Governance Program as follows:
8.1 Data Governance Program
The University shall establish a Data Governance Program to guide the strategic use, management, and reporting of University Data and to manage the quality, consistency, usability, accessibility, availability, and protection of university data throughout its lifecycle. The Data Governance Program shall ensure that University Data are used in compliance with federal, state, and local regulations, applicable Tulane University policies, and relevant contractual obligations. The Data Governance Program shall include human capital systems designed to educate those with access to data regarding proper use and protection. The structure of the Data Governance Program includes the following:
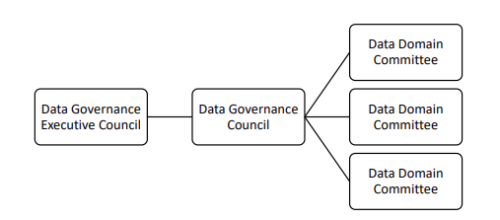
8.1.a. Data Governance Executive Council
The Data Governance Executive Council establishes overall policies for management and access to University Data. This committee shall be composed of the Data Trustees; shall be chaired by the Chief Administrative Data Management Officer; shall approve the policies and procedures developed in each functional area by the Data Stewards and Data Trustees to ensure appropriate compliance with this policy and applicable regulations; shall provide oversight of all University processes which capture, maintain, and report on Administrative Data; and shall approve any decisions to archive Administrative Data.
8.1.b. Data Governance Council
The Data Governance Council establishes overall policies for management and access to University Data. This committee shall be composed of the Data Trustees; shall be chaired by an elected member of the Data Governance Council; shall approve the policies and procedures developed in each functional area by the Data Stewards and Data Trustees to ensure appropriate compliance with this policy and applicable regulations; shall provide oversight of all University processes which capture, maintain, and report on Administrative Data; and shall approve any decisions to archive Administrative Data.
8.1.c. Data Domain Committees
Data Domain Committees are comprised of Data Stewards for a designated data domain (e.g., “Academics and Student Data”). Data Domain Committees meet regularly to anchor the people, process, and technology change needed to address domain-specific issues by eliciting the concerns of others and taking into consideration the needs of the entire University. The committee provides a forum for the committee members to prioritize their collective data needs, coordinate their efforts, and establish common processes and procedures that enhance any policies and procedures enacted by the Data Governance program overall.
8.2 Data Lifecycle and Data Handling
Data Trustees, Data Stewards, Data Consumers, and Data Custodians are collectively responsible for the management of all University Data throughout the data lifecycle. The university shall issue policies, standards, and procedures as appropriate that address the quality, consistency, usability, accessibility, availability, and protection of university information resources and data throughout its lifecycle and according to classification level. More information on data lifecycle and data handling is outlined in the Tulane University Data Management Policy.
8.3 Data Classification
Identification and classification of University Data are essential for ensuring that the appropriate degree of protection is applied to University Data. University Data is classified into four categories:
- Level 1 - Public
- Level 2 - Internal
- Level 3 - Confidential
- Level 4 Restricted
The classification scheme applies to all University Data both physical and electronic and will inform the baseline security controls for protection of the data. The classification of specific University Data is subject to change based on risk assessment and as the attributes of that data change (e.g., its elements, content, uses, importance, method of transmission, or regulatory context).
Reference the Data Classification Policy for additional data classification guidelines.
8.4 Data Security
Improper use of university data can result in risk to the University. University Data must be safeguarded and managed throughout its lifecycle in all formats and media (e.g., print and digital), at all points of access, and across all University systems through coordinated efforts and shared responsibilities. In collaboration with Data Trustees, Stewards, and Custodians, the Vice President, Information Technology and Chief Information Officer shall guide the administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to apply to the handling, use, transmission, processing, storage, and destruction of University Data through officially supported University Information Systems.
Consequence of Violating the Policy
Violation of this policy may result in disciplinary action, up to and including termination.
Failure to comply with the data governance standards outlined here and in related policies may result in harm to individuals, organizations, or the University. Violations of this policy or any law related to the use of University Data, including, but not limited to the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act of 1974 (FERPA), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), may result in penalties and disciplinary action under rules established by Tulane University.
Tulane Data Governance Applicable Laws and Regulations
Related laws and regulations include:
- The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act of 1974 (FERPA) was enacted, among other purposes, to protect the privacy of students' education records. The “education records” are defined as those records, files, documents, and other materials that contain information directly related to a student and that are maintained by the University or by a third party acting for the university. The form in which the information is maintained by the University does not matter. For example, computerized or electronic files, audio or videotape, photographic images, and film, with such information are "education records". This includes communications and documents distributed or received by email, or other similar University systems, which are retained in these systems, either by the sending or receiving party. See the University’s FERPA-related resources for additional guidance: https://registrar.tulane.edu/privacy-policies-forms.
- The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), short-form for the Financial Modernization Act of 1999, was enacted to promote financial integration and develop a regulatory framework for financial institutions which deal with non-public financial information, such as financial aid, Bursar activities, faculty housing finances, and donations to the university. This financial information can be provided by the consumer, initiated by the University, or received from another financial institution. See the University’s GLBA-related resources https://it.tulane.edu/guidelines-allcomputer-systems-handling-credit-ca… for additional guidance
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, complex legislation, and various Rules signed into law in 1996 and updated over the years require safeguarding individually identifiable health information, especially for privacy and security. EPHI is Electronic Protected Health Information that TULANE UNIVERSITY creates, receives, maintains, and/or transmits electronically. It can exist outside a computer, such as on clinical equipment, storage media, tapes, DVDs, and many other peripheral devices. See the University’s HIPAA-related resources for additional guidance: https://it.tulane.edu/hipaa-security-policies & https://counsel.tulane.edu/upo/hipaa-privacy-policies-procedures-forms
- The European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a European Union (EU) law that requires organizations that collect data on European citizens to comply with laws regarding protecting that data. In addition, the GDPR gives EU individuals certain rights regarding how their information can be used. See the University’s GDPR Privacy Policy for additional guidance: https://tulane.edu/gdpr-privacy-policy
- The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of requirements issued by the major credit card brands intended to ensure that all entities that process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. Credit/Debit Card numbers and other cardholder information are subject to specific industry standards and additional controls and, thus, must be handled appropriately. See the University’s Payment Card Industry Data Security guidelines: https://it.tulane.edu/guidelines-all-computer-systems-handling-credit-c…
All IT Tulane policies are here
Information System Risk Criticality Classification Policy - currently in draft form
Data and System Security Policy - currently in draft form
Governance and Retention of Research Data Policy - currently in draft form
